The waves are refracted as they travel through the earth due to a change in density of the medium. Anomalously hot areas slow down seismic waves.
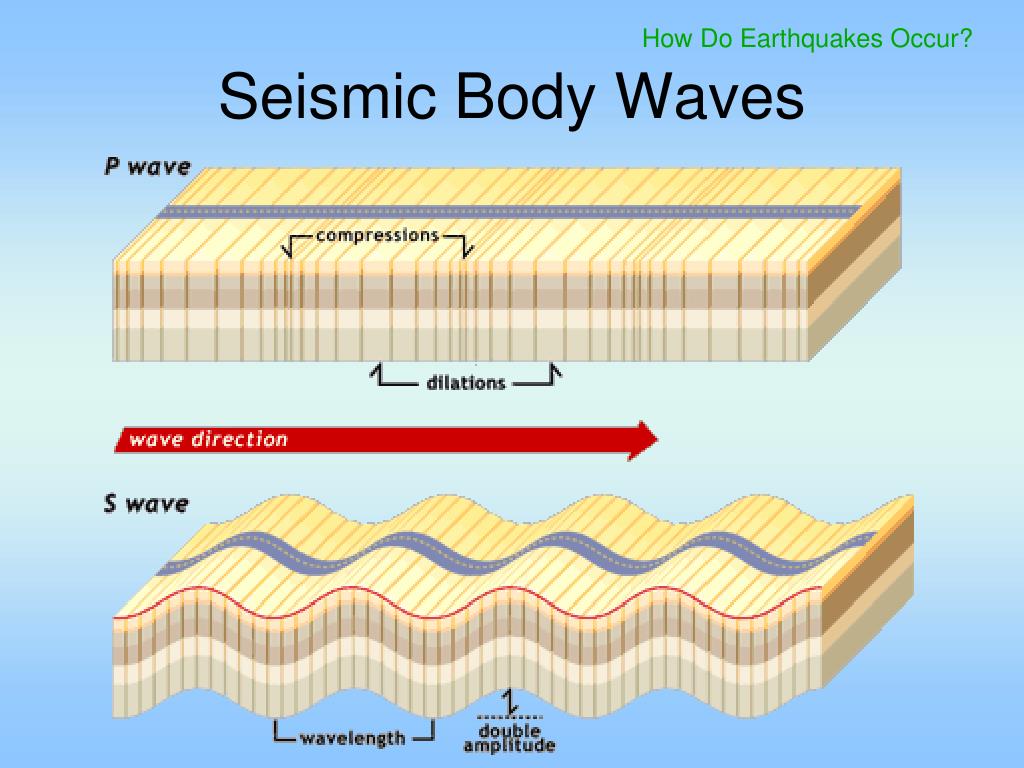
Why Does Seismic Waves Change Direction, As an s wave passes through a material, the site of its passing moves from side to side or up and down (as compared to the direction the wave is traveling). Compressive waves compress or rarify the density of the material in the direction of the wave travel.

Longitudinal waves because the displacement of the medium is in the same direction as, or the opposite direction to, (parallel to) the direction of propagation of the wave; But if the wave goes through the boundary and just gets bent a little bit, its direction changes, that is refraction. Seismic waves gradually bend and change speed as the density of rock changes. Using the parameterizations of priestley and mckenzie (2006) as a first attempt to assess the role of temperature alone on seismic velocity, the velocity change of 0.1 km s − 1 at 150 km depth between 52 and 110 my and > 110 my would require cooling in.
Anomalously hot areas slow down seismic waves.
P, primary, or compressional waves travel the fastest (~6 km/sec in the upper crust). As we know from physics, all waves change direction when they pass through layers of different density (refraction). The velocity of seismic waves is directly related to the density of a rock. Let me just make that clear. At depths of less than 25 kilometers (16 miles), compressional waves travel at about 6.8 kilometers (4.2 miles) per second. That is what makes light collect in a magnifying glass, and that is also what makes seismic waves travel in curved paths through the earth (because of the increasing pressure, materials are more dense towards the core, travel.
 Source: slideshare.net
Source: slideshare.net
Seismic waves change speed as they travel through different materials. The epicenter of an earthquake sends out waves which are like an object dropped on to a still body of water that sends out ripples. Let me just make that clear. P, primary, or compressional waves travel the fastest (~6 km/sec in the upper crust). What are the different types.
 Source: slideserve.com
Source: slideserve.com
When the waves cross the boundary between two different layers, there is a sudden change in direction due to refraction. Seismic waves travel at different speeds through different materials. Reflection is when it bounces back. (this image was vor conductivity but it serves the point.) at the interface. These cause thermal and compositional diffusion and result in attenuation.
 Source: slideserve.com
Source: slideserve.com
Seismic waves are usually generated by movements of the earth’s tectonic plates but may also be caused by explosions, volcanoes and landslides. Seismic waves travel a curving path through the earth due to changes in composition, pressure, and temperature within the layers of the earth. The speed of p waves and s waves increases as they travel deeper into the.
 Source: science8sc.weebly.com
Source: science8sc.weebly.com
P, primary, or compressional waves travel the fastest (~6 km/sec in the upper crust). But if the wave goes through the boundary and just gets bent a little bit, its direction changes, that is refraction. Seismic waves travel at different speeds through different materials. This change in direction can result in either the refraction or reflection of the wave. Which.
 Source: slideshare.net
Source: slideshare.net
Why do seismic waves change direction? Refraction is when it gets deflected a little bit. Secondary , or s waves, travel slower than p waves and are also called shear waves because they don�t change the volume of the material through which they propagate, they shear it. They cause the matter to oscillate forward and backward, parallel to the motion.
 Source: slideshare.net
Source: slideshare.net
Longitudinal waves because the displacement of the medium is in the same direction as, or the opposite direction to, (parallel to) the direction of propagation of the wave; The light wave not only changes directions at the boundary, it also speeds up or slows down and transforms into a wave with a larger or a shorter wavelength. When an earthquake.
 Source: slideserve.com
Source: slideserve.com
This change in direction can result in either the refraction or reflection of the wave. Anomalously hot areas slow down seismic waves. “transverse” comes from the latin words for “turned across.”) s waves cannot travel through liquids or gases. At depths of less than 25 kilometers (16 miles), compressional waves travel at about 6.8 kilometers (4.2 miles) per second. Seismic.
 Source: officersiasacademy.blogspot.com
Source: officersiasacademy.blogspot.com
They travel through the earth in curved paths, but they change. “transverse” comes from the latin words for “turned across.”) s waves cannot travel through liquids or gases. P, primary, or compressional waves travel the fastest (~6 km/sec in the upper crust). We have to look at the incident wave as an excitor at the interface, which will give us.
 Source: chegg.com
Source: chegg.com
Therefore as they travel from one medium into another, they change speed. Let me just make that clear. Seismic waves gradually bend and change speed as the density of rock changes. Why do seismic waves change direction? Their direction also changes as they reflect or refract when coming across materials with different densities.
 Source: slideserve.com
Source: slideserve.com
Primary waves are called so because they are the fastest among the seismic waves and hence are recorded first on the seismograph. Therefore as they travel from one medium into another, they change speed. But if the wave goes through the boundary and just gets bent a little bit, its direction changes, that is refraction. Different parts of the earths.
 Source: slideserve.com
Source: slideserve.com
This causes the waves to travel in curved paths. Using the parameterizations of priestley and mckenzie (2006) as a first attempt to assess the role of temperature alone on seismic velocity, the velocity change of 0.1 km s − 1 at 150 km depth between 52 and 110 my and > 110 my would require cooling in. Sound waves in.
 Source: slideshare.net
Source: slideshare.net
They cause the matter to oscillate forward and backward, parallel to the motion of the seismic wavefront. Increase with depth, even if the lithology does not change. The more elastic the material is, the higher is the velocity. As we know from physics, all waves change direction when they pass through layers of different density (refraction). When the waves cross.
 Source: slideserve.com
Source: slideserve.com
After the stone hits the water ripples move outwards from the centre in every direction. The only time that a wave can be transmitted across a boundary, change its speed, and still not refract is when the light wave approaches the boundary in a direction that is perpendicular to it. The velocity of seismic waves is directly related to the.
 Source: slideshare.net
Source: slideshare.net
Using the parameterizations of priestley and mckenzie (2006) as a first attempt to assess the role of temperature alone on seismic velocity, the velocity change of 0.1 km s − 1 at 150 km depth between 52 and 110 my and > 110 my would require cooling in. When the waves cross the boundary between two different layers, there is.
 Source: scienceexchange.caltech.edu
Source: scienceexchange.caltech.edu
Shear waves push the solid side to side orthogonal to the direction of wave travel. As seismic waves travel, they cause an adiabatic pressure perturbation, which causes a temperature change and, potentially, freezing and melting. At depths of less than 25 kilometers (16 miles), compressional waves travel at about 6.8 kilometers (4.2 miles) per second. Seismic wave studies have allowed..
 Source: slideshare.net
Source: slideshare.net
(this image was vor conductivity but it serves the point.) at the interface. What are the different types of seismic waves? At depths of less than 25 kilometers (16 miles), compressional waves travel at about 6.8 kilometers (4.2 miles) per second. This causes the waves to travel in curved paths. They cause the matter to oscillate forward and backward, parallel.
 Source: faculty.buffalostate.edu
Source: faculty.buffalostate.edu
This is why s waves are also known as transverse waves. The waves are refracted as they travel through the earth due to a change in density of the medium. Seismic waves change speed and direction when they encounter different materials is a true statement. This causes the waves to travel in curved paths. P waves push (compress) and pull.
 Source: slideserve.com
Source: slideserve.com
Seismic waves change speed and direction when they encounter different materials is a true statement. P, primary, or compressional waves travel the fastest (~6 km/sec in the upper crust). The velocity of seismic waves is directly related to the density of a rock. Seismic wave studies have allowed. Seismic waves change speed as they travel through different materials.
 Source: slideshare.net
Source: slideshare.net
When an earthquake occurs, the shockwaves of released energy that shake the earth and temporarily turn soft deposits, such as clay, into jelly (liquefaction) are called seismic waves, from the greek ‘seismos’ meaning ‘earthquake’. When the waves cross the boundary between two different layers, there is a sudden change in direction due to refraction. You can learn about this in.
 Source: esccalbe.blogspot.com
Source: esccalbe.blogspot.com
Reflection is when it bounces back. “transverse” comes from the latin words for “turned across.”) s waves cannot travel through liquids or gases. These cause thermal and compositional diffusion and result in attenuation. Seismic waves travel more quickly through denser materials and therefore generally travel more quickly with depth. This change in direction can result in either the refraction or.
 Source: slideserve.com
Source: slideserve.com
Seismic waves travel a curving path through the earth due to changes in composition, pressure, and temperature within the layers of the earth. Anomalously hot areas slow down seismic waves. The epicenter of an earthquake sends out waves which are like an object dropped on to a still body of water that sends out ripples. When an earthquake occurs, the.
 Source: slideserve.com
Source: slideserve.com
The velocity of seismic waves is directly related to the density of a rock. Seismic waves travel a curving path through the earth due to changes in composition, pressure, and temperature within the layers of the earth. As seismic waves pass through the earth, they are refracted, or bent, like rays of light bend when they pass through a glass.
 Source: geologylearn.blogspot.com
Source: geologylearn.blogspot.com
There are two types of body waves. Primary waves are called so because they are the fastest among the seismic waves and hence are recorded first on the seismograph. They travel through the earth in curved paths, but they change. Seismic waves travel at different speeds through different materials. So if i have some type of boundary here, and i.
 Source: slideserve.com
Source: slideserve.com
Secondary , or s waves, travel slower than p waves and are also called shear waves because they don�t change the volume of the material through which they propagate, they shear it. As we know from physics, all waves change direction when they pass through layers of different density (refraction). Let me just make that clear. What are the different.
 Source: calacademy.org
Source: calacademy.org
There are two types of body waves. The more elastic the material is, the higher is the velocity. But if the wave goes through the boundary and just gets bent a little bit, its direction changes, that is refraction. Seismic velocities depend on the material properties such as composition, mineral phase and packing structure, temperature, and pressure of the media.